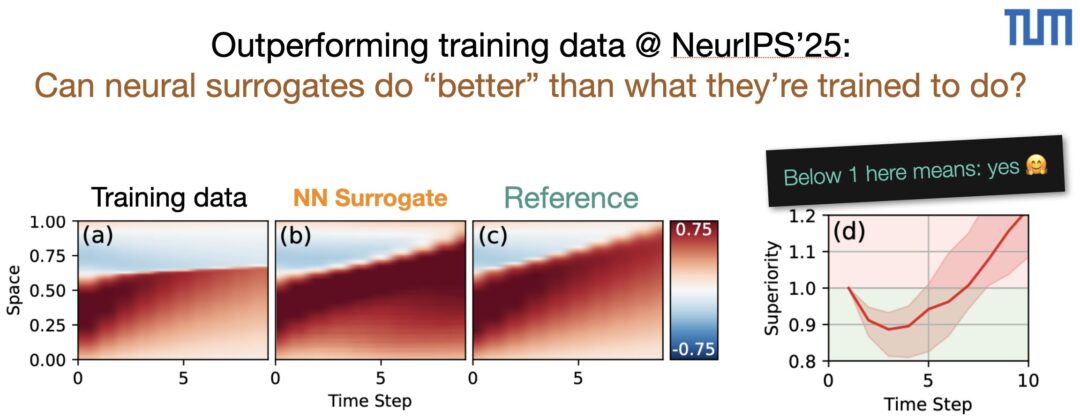
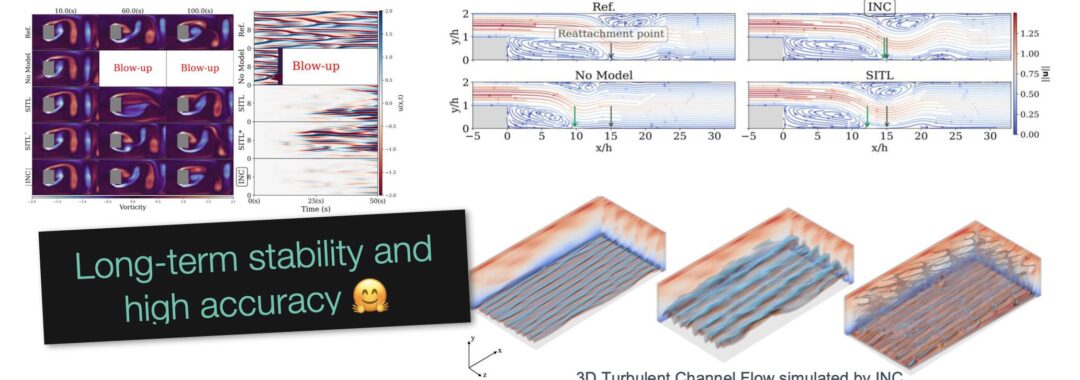
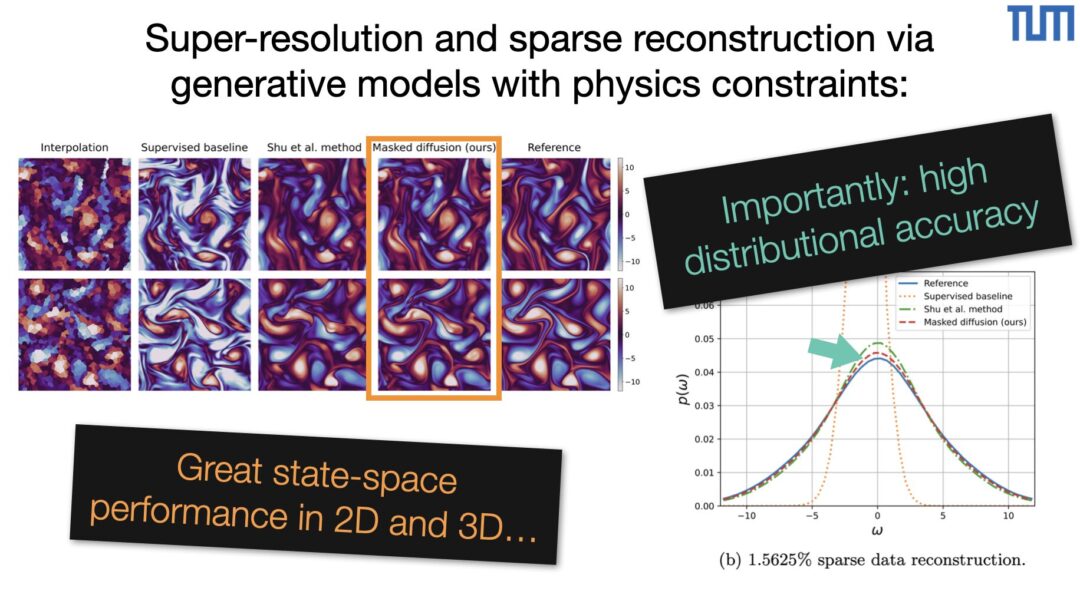
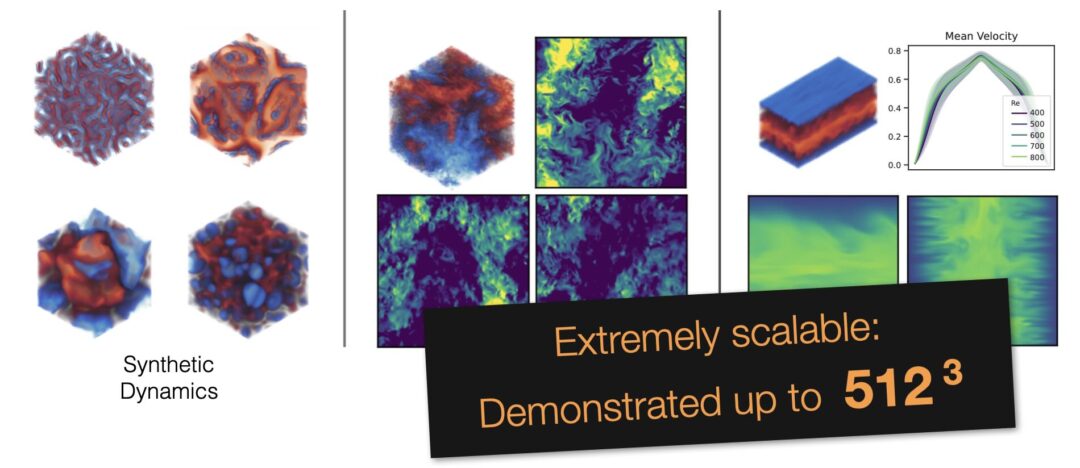
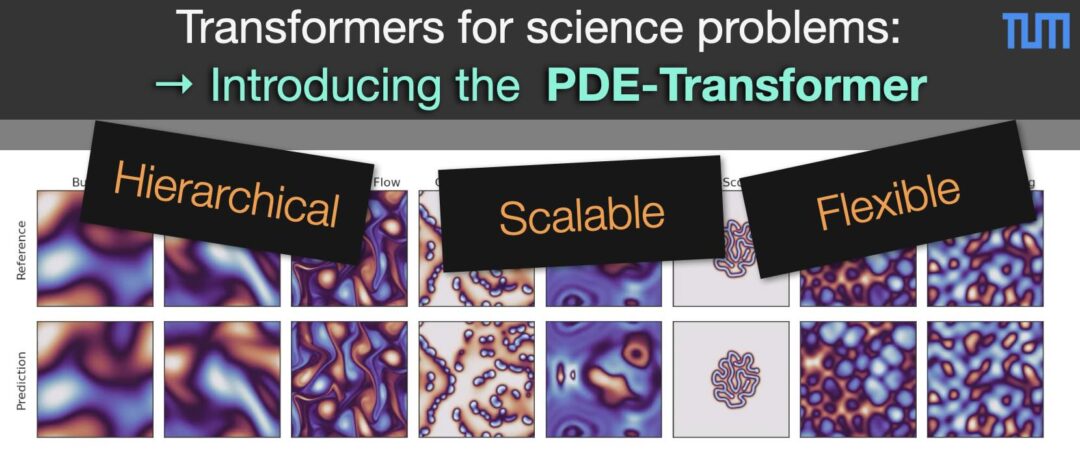
We’re happy to report that our Physics-based Flow Matching framework got an accept for ICLR’26! We target the fundamental trade-off between physical consistency and distributional fidelity in generative modeling by proposing Physics-Based Flow Matching (PBFM): a principled framework that explicitly targets Pareto-optimal solutions between physics-constraints and data-driven objectives.
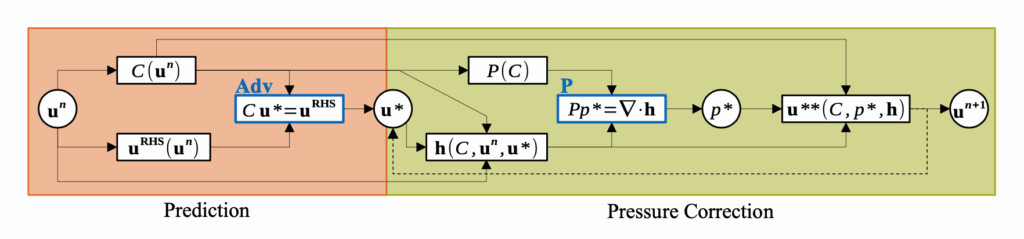
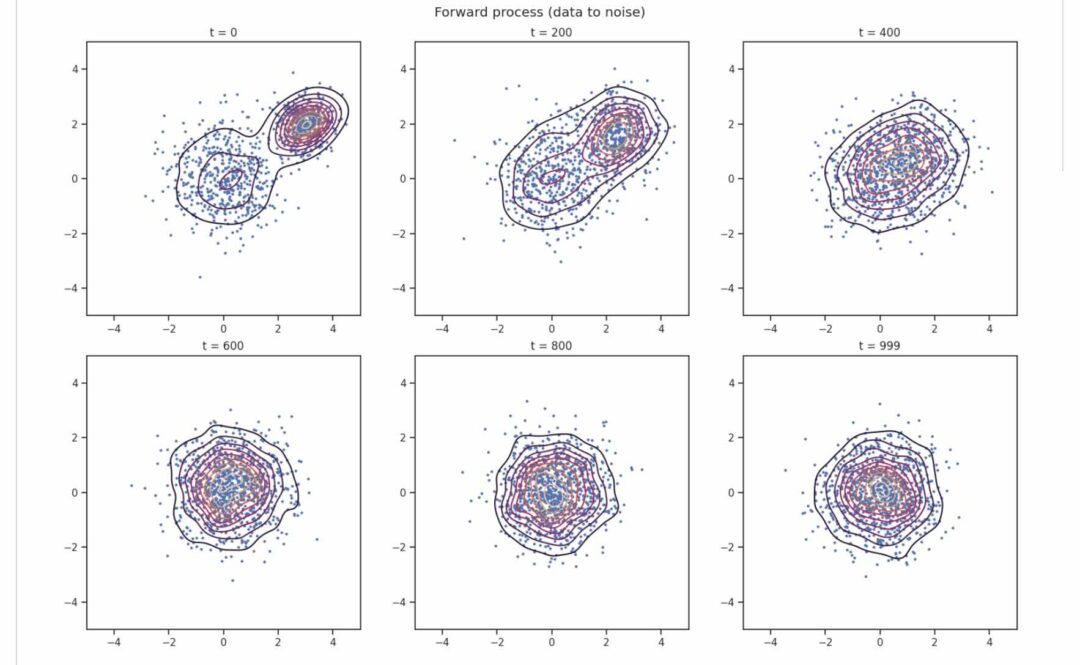
- PBFM builds on flow matching and enforces PDE and algebraic constraints during training using conflict-free gradient updates via the ConFIG optimizer. We address the long-standing Jensen’s gap by unrolling the learned dynamics during training, ensuring that physical residuals are evaluated on accurate final samples, without slowing down inference.
- Across three challenging benchmarks (Darcy, Kolmogorov flows, and highly nonlinear dynamic stall), PBFM consistently advances the Pareto front, achieving lower physical residuals and better distributional accuracy than prior physics-informed diffusion and flow-based methods. At the same time, it preserves the key advantage of flow matching: fast, scalable inference, with performance comparable to unconstrained generators.
- We frame physics-constrained generative modeling as a multi-objective optimization problem to deliver a practical solution. PBFM demonstrates that high-fidelity uncertainty-aware generative models can be both physically meaningful and statistically correct; this makes them a powerful tool for real-world applications in science and engineering.
Code and paper can be found here: https://github.com/tum-pbs/PBFM/ , https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.08604